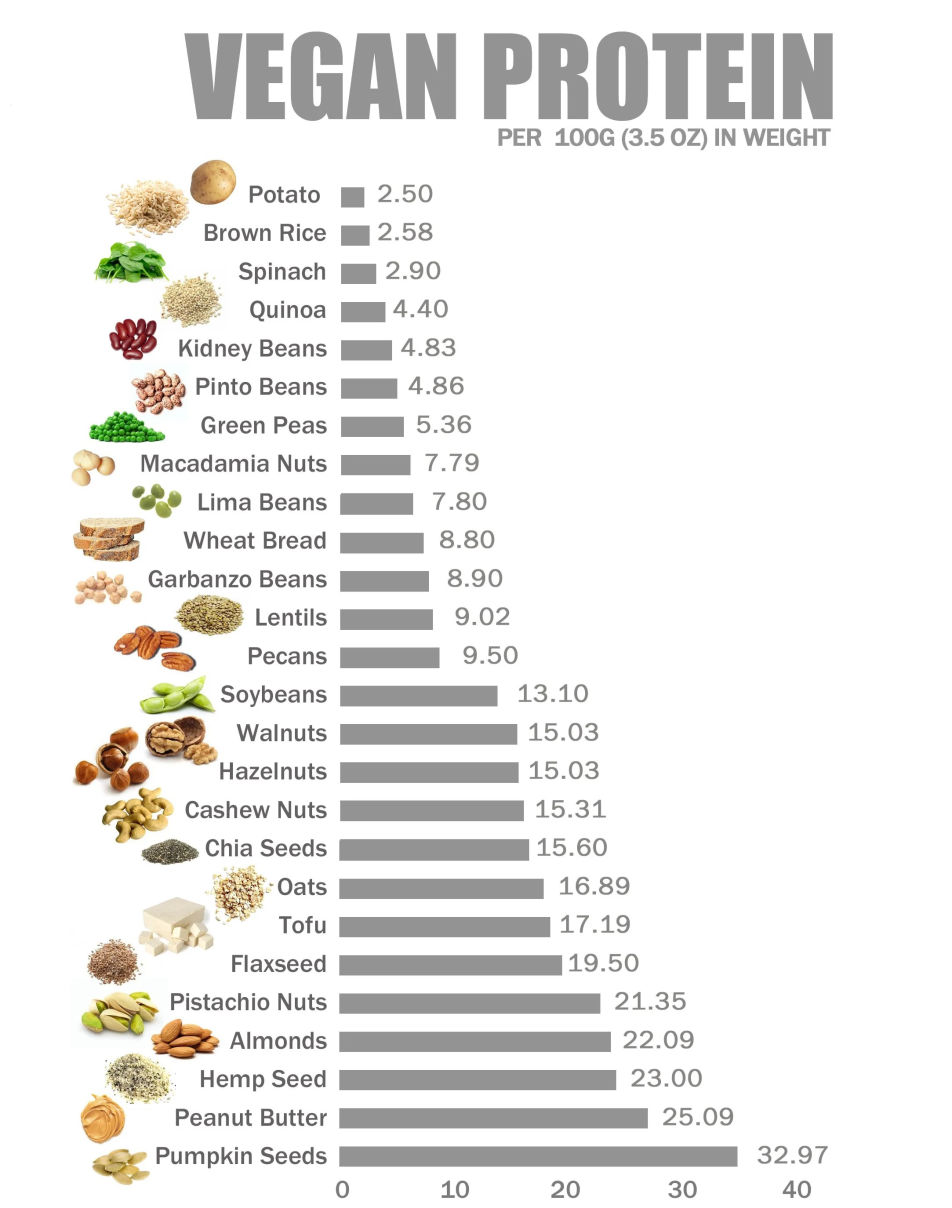
Protein for Vegans:
Basic Information
In the past, during the 1970s and 1980s, there was a prevailing belief that vegetarians and vegans were at high risk of protein deficiency. This concern largely stemmed from the influential book "Diet for a Small Planet" by Frances Moore Lappé, published in 1971. However, looking back, the book's protein recommendations were unnecessarily strict.
Today, the perception has swung too far in the opposite direction. Some vegans dismiss the importance of protein, and it can even be subject to mockery among certain individuals.
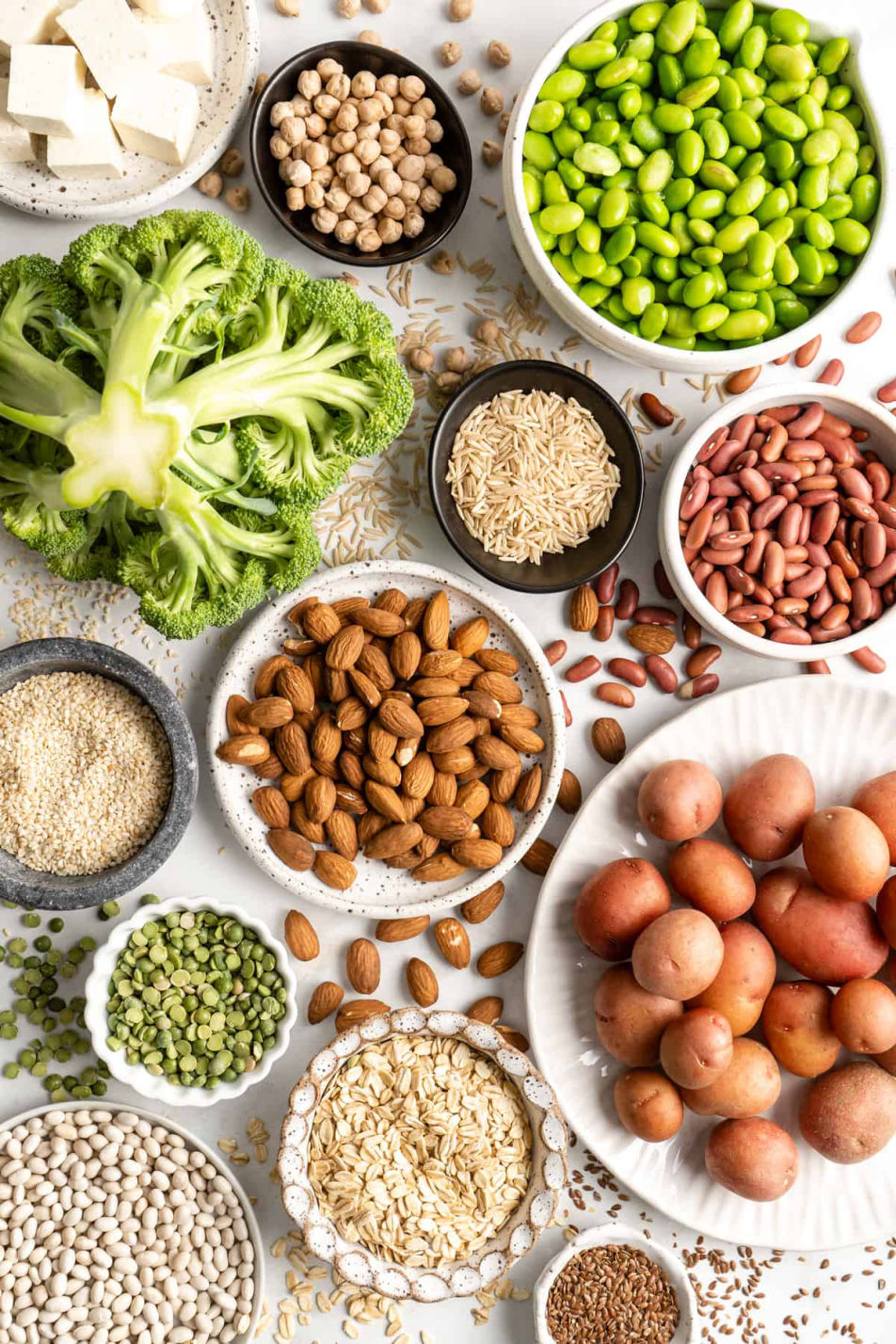
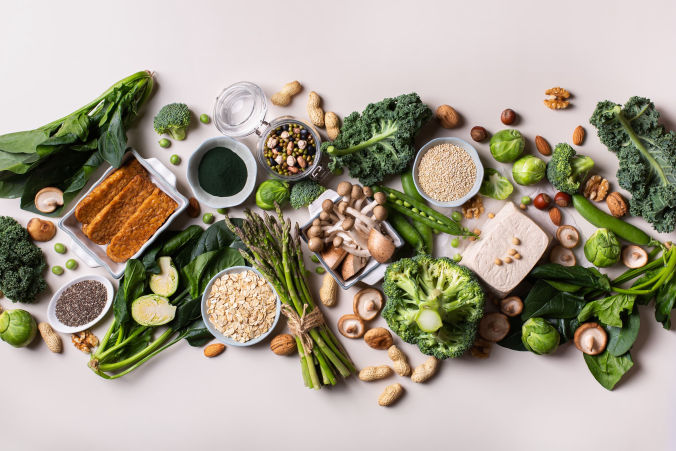
However, downplaying the significance of protein is entirely misguided. While it is true that vegans can easily obtain sufficient protein, many fall short in their intake. Therefore, if you follow a vegan or predominantly plant-based diet, it is risky to disregard the importance of protein.